Digital Geometry Processing
Exercise5-OpenMesh
Heng Liu, liu@inf.unibe.ch
Computer Graphics Group
OpenMesh
- Features
- Representation of arbitrary polygonal (the general case) and pure triangle meshes (providing more efficient, specialized algorithms)
- Explicit representation of vertices, halfedges, edges and faces.
- Fast neighbourhood access, especially the one-ring neighbourhood.
- Highly customizable :
- Choose your coordinate type (dimension and scalar type)
- Attach user-defined elements/functions to the mesh elements.
- Attach data at runtime using dynamic properties.
Halfedge data structure
- Vertex
- one outgoing halfedge
- Halfedge
- to vertex
- incident face
- previous/ next/ opposite halfedges
- Face
- one incident halfedge
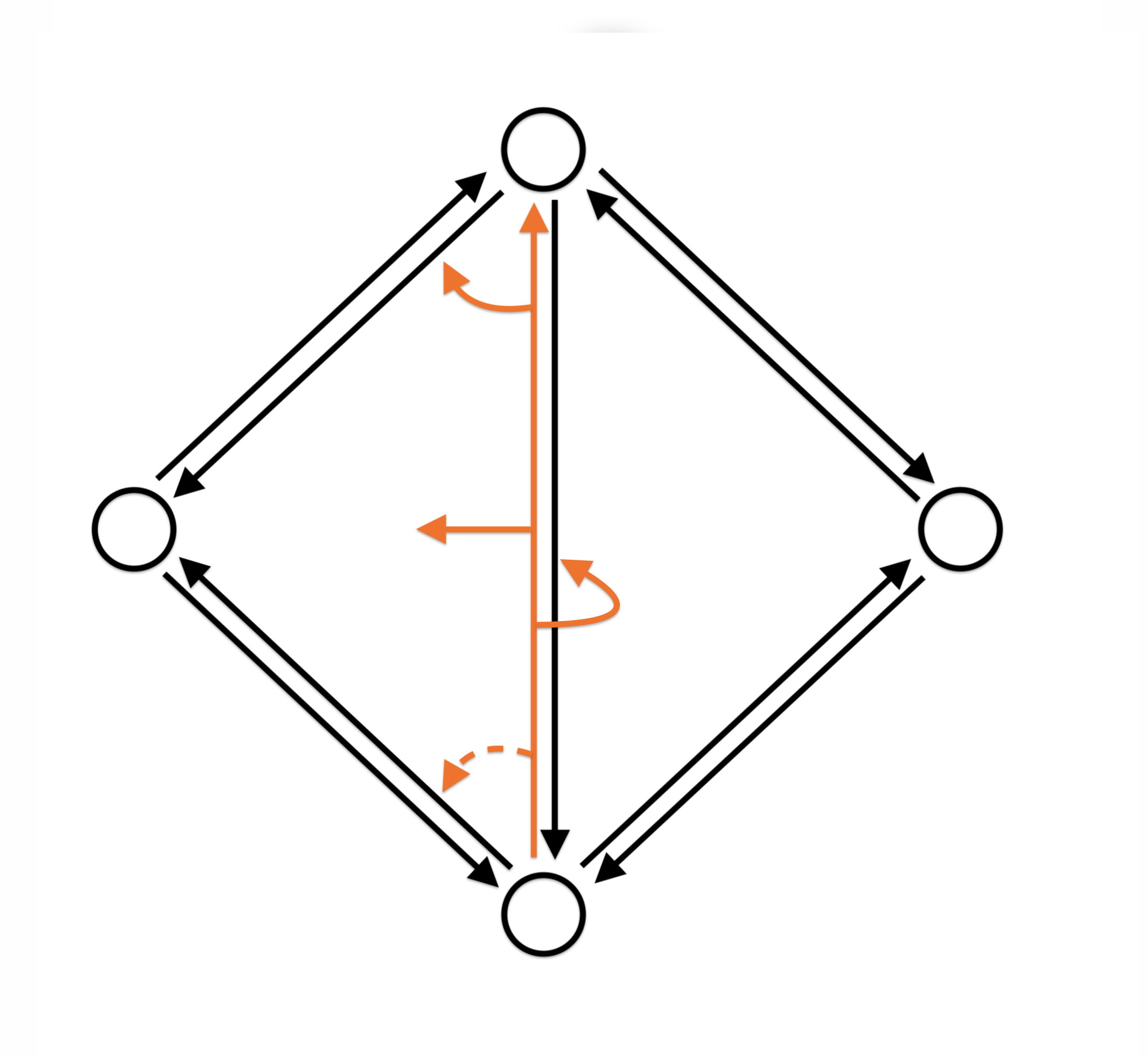
Halfedge data structure
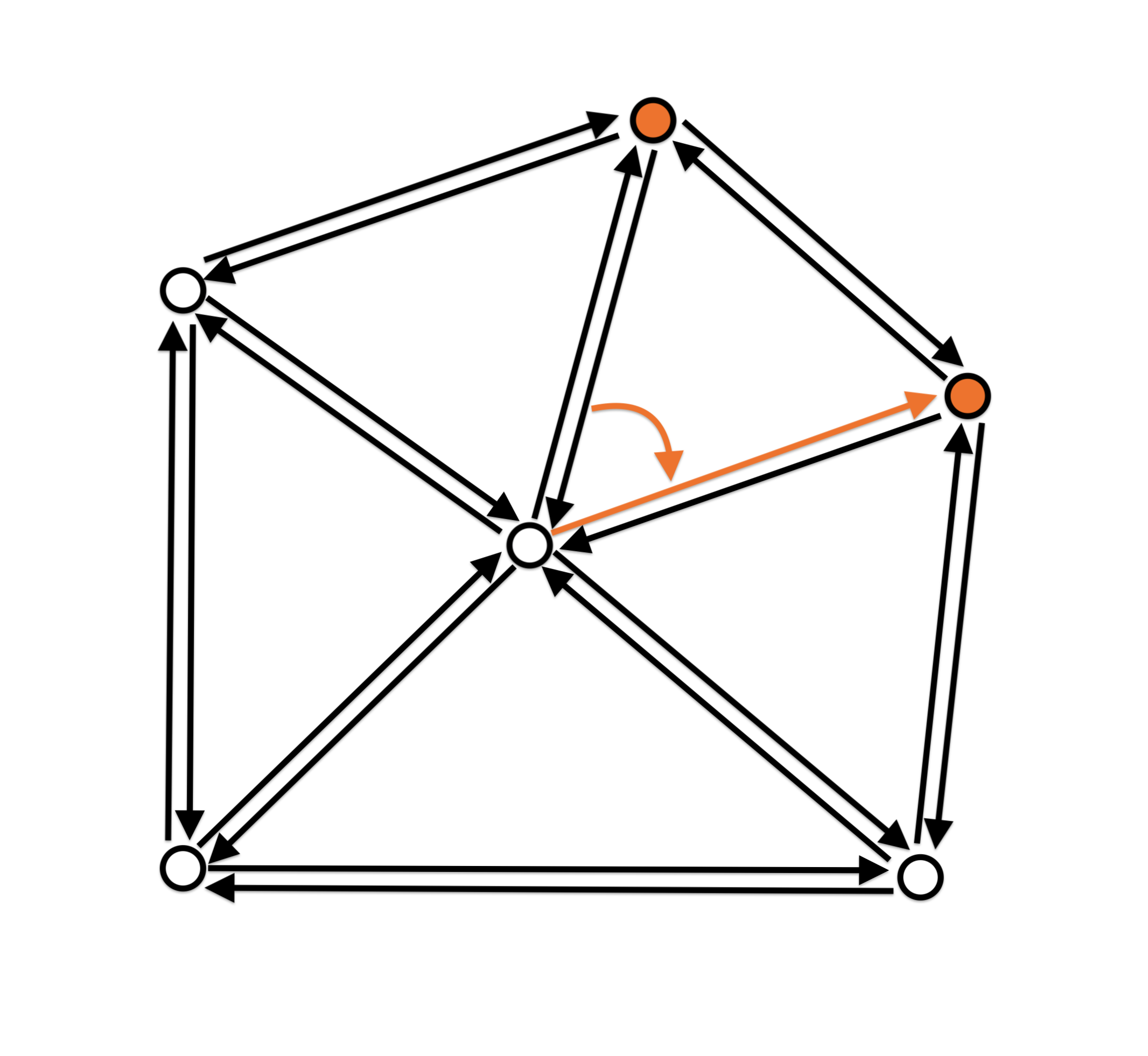
- One-ring neighbourhood traversal
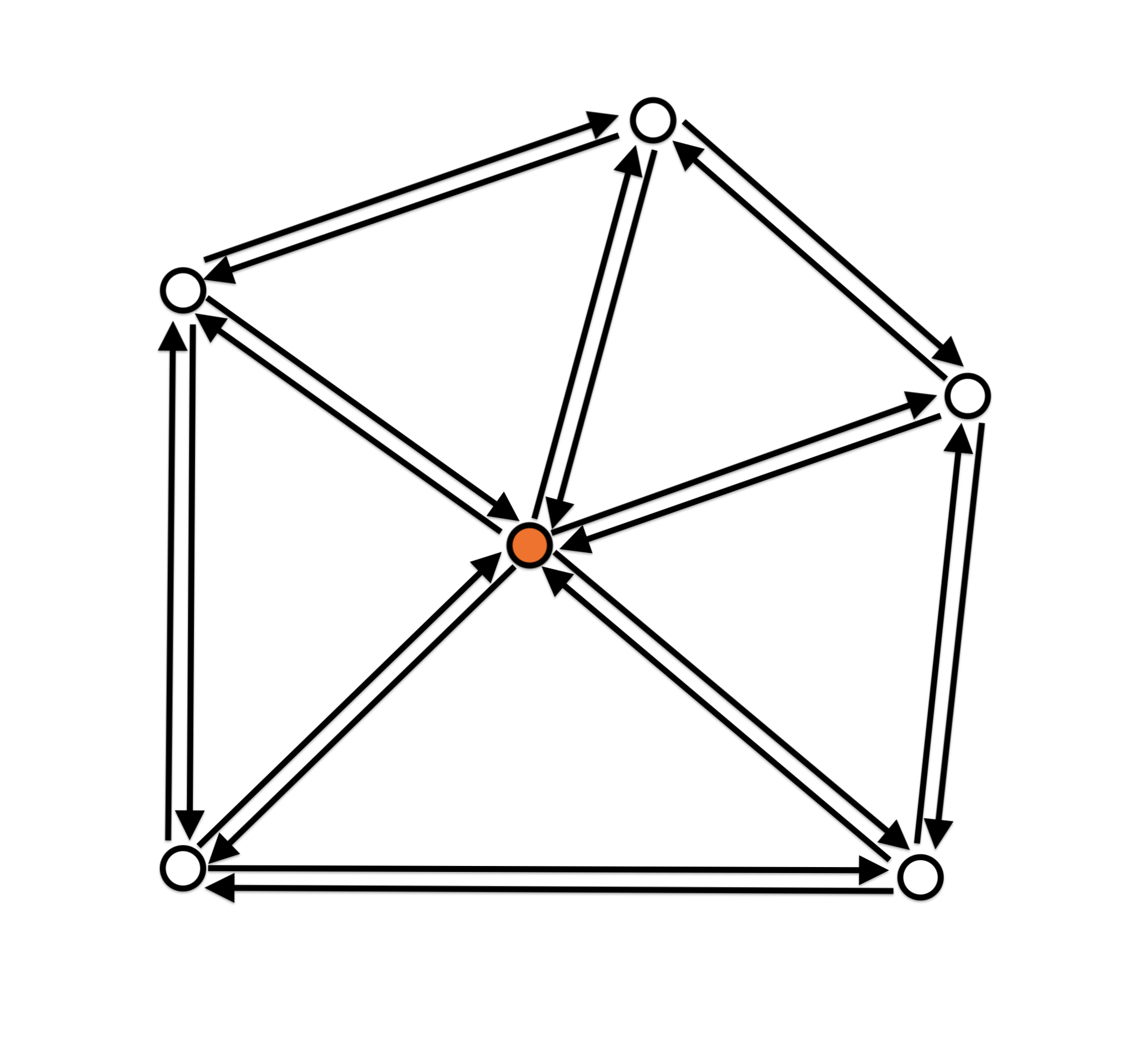
Halfedge data structure
- One-ring neighbourhood traversal
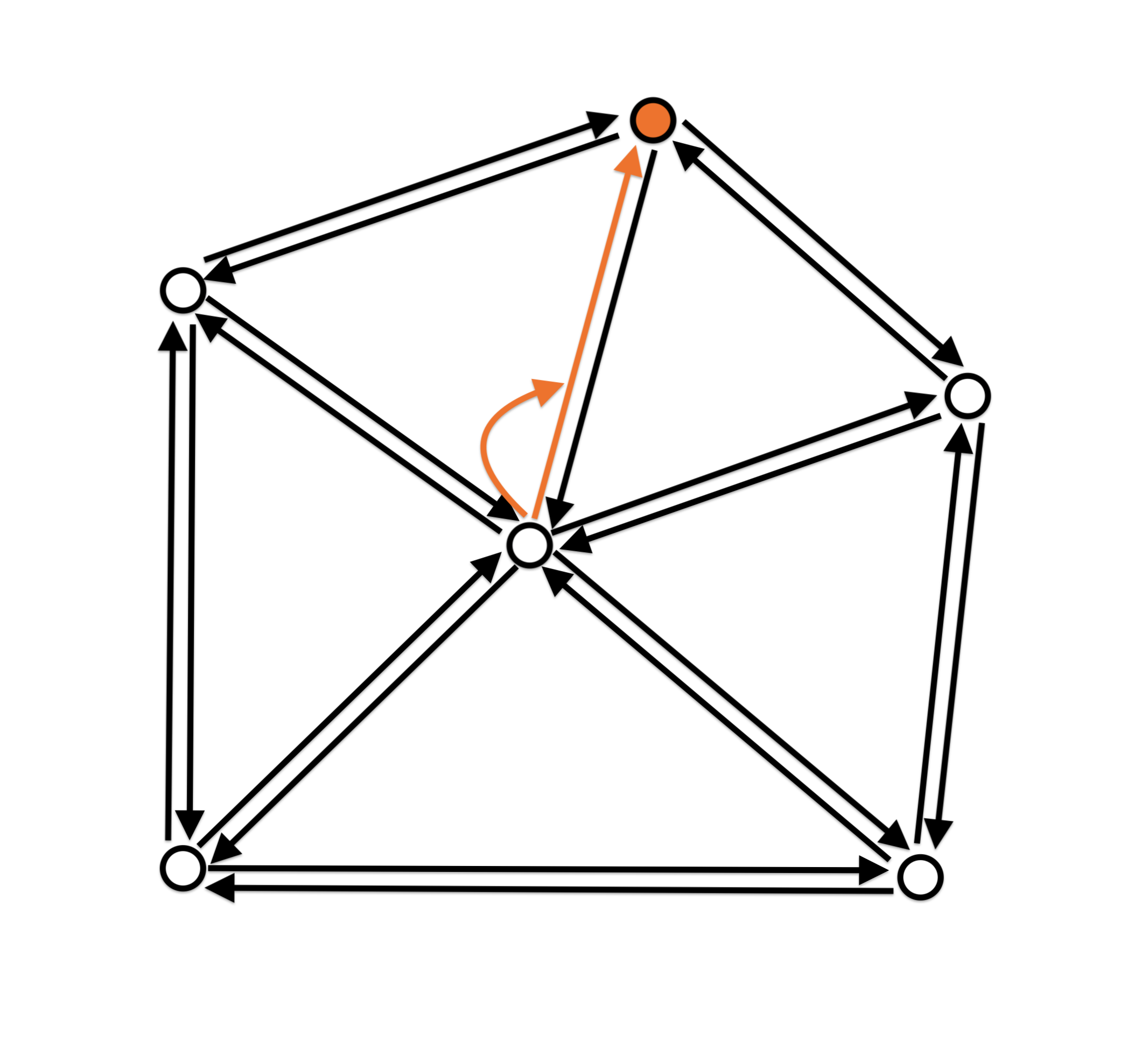
Halfedge data structure
- One-ring neighbourhood traversal
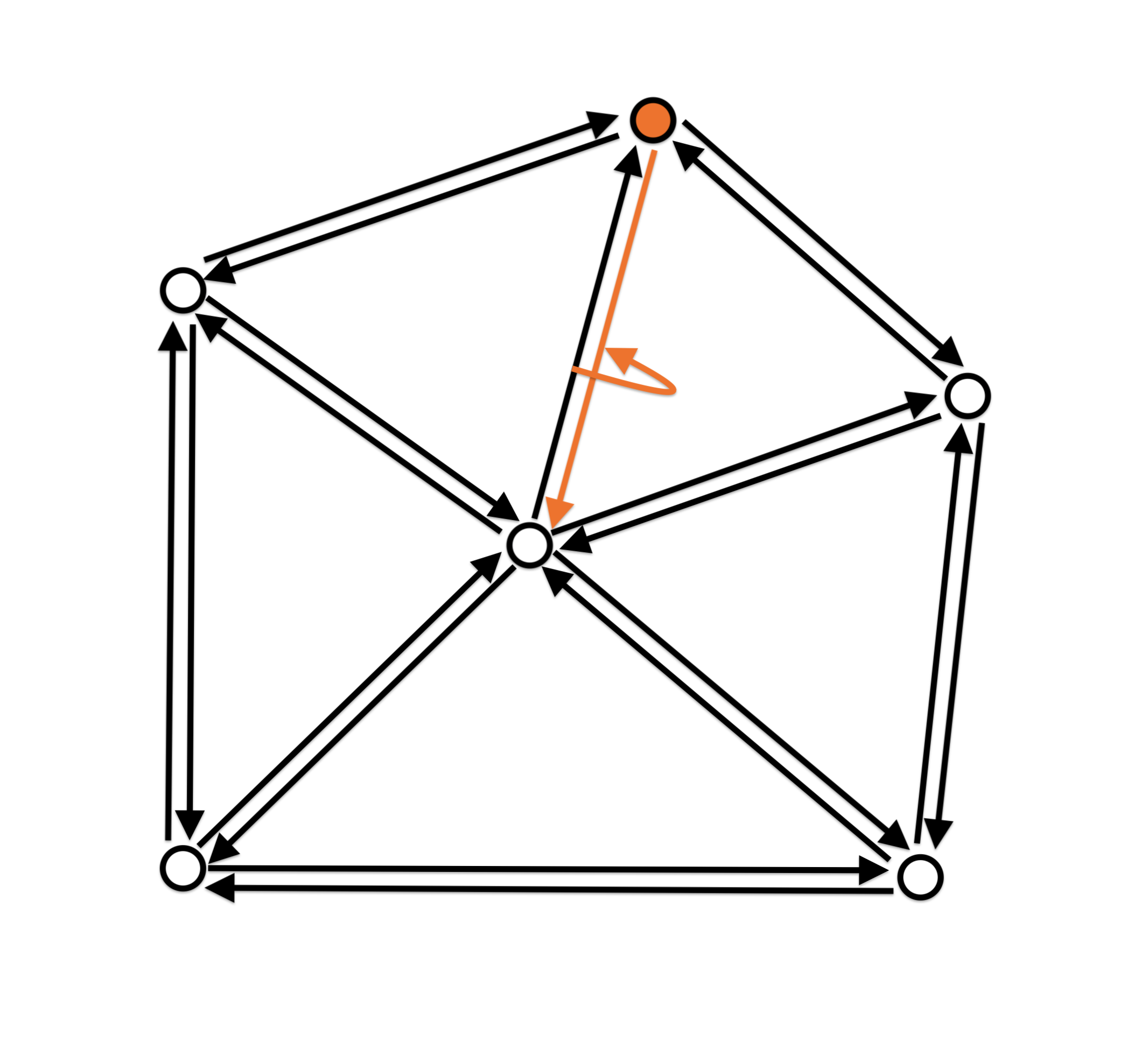
Halfedge data structure
- One-ring neighbourhood traversal
TriMesh definition
- Define with default traits
typedef OpenMesh::TriMesh_ArrayKernelT<> MyMesh;
MyMesh mesh;- Define with customized traits
struct TriTraits : public OpenMesh::DefaultTraits
{
/// Use double precision points
typedef OpenMesh::Vec3d Point;
/// Use double precision Normals
typedef OpenMesh::Vec3d Normal;
/// Use RGBA Color
typedef OpenMesh::Vec4f Color;
};
typedef OpenMesh::TriMesh_ArrayKernelT<TriTraits> MyMesh;
MyMesh mesh;Mesh creation
- Adding a vertex
MyMesh mesh;
...
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(x,y,z));- Adding a face
MyMesh mesh;
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh0, vh1, vh2;
...
OpenMesh::FaceHandle fh = mesh.add_face(vh0, vh1, vh2);Access vertex geometry
- Reading vertex positions
MyMesh mesh;
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh;
...
MyMesh::Point pos = mesh.point(vh);- Modifying vertex positions
MyMesh mesh;
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh;
MyMesh::Point new_pos;
...
mesh.set_point(vh, new_pos);Mesh elements traversal
- How to modify all vertices?
MyMesh mesh;
//vertex iterators
MyMesh::VertexIter v_it, v_begin, v_end;
//range of iterators
v_begin = mesh.vertices_begin();
v_end = mesh.vertices_end();
//iterate over all vertices
for(v_it = v_begin; v_it != v_end; ++v_it){
//get vertex handle
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh = *v_it;
//process the vertex
DoSomethingWithVertex(vh);
}Mesh elements traversal
- Iterating over faces
- MyMesh::VertexIter -> MyMesh::FaceIter
- vertices_begin() -> faces_begin()
- vertices_end() -> faces_end()
- Similarly:
- MyMesh::EdgeIter & MyMesh::HalfedgeIter
Enumerating incident elements
Iterate over all neighbouring vertices
MyMesh mesh; OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh; //circulator around a vertex MyMesh::VertexVertexIter vv_it = mesh.vv_iter(vh); // circulate around the current vertex for(; vv_it.is_valid(); ++vv_it) { //process the neighbouring vertex DoSomethingWithVertex(*vv_it); }
Enumerating incident elements
- The circulators around a vertex are:
- VertexVertexIter: iterate over all neighboring vertices.
- VertexIHalfedgeIter: iterate over all incoming halfedges.
- VertexOHalfedgeIter: iterate over all outgoing halfedges.
- VertexEdgeIter: iterate over all incident edges.
- VertexFaceIter: iterate over all adjacent faces.
Enumerating incident elements
- The circulators around a face are:
- FaceVertexIter: iterate over the face’s vertices.
- FaceHalfedgeIter: iterate over the face’s halfedges.
- FaceEdgeIter: iterate over the face’s edges.
- FaceFaceIter: iterate over all edge-neighboring faces.
Element count functions
- Query entity number
MyMesh mesh;
unsigned int n1 = mesh.n_vertices(),
n2 = mesh.n_faces(),
n3 = mesh.n_edges(),
n4 = mesh.n_halfedges();Using properties
- Template based properties
MyMesh mesh;
//define a property type, e.g edge property in float
typedef OpenMesh::EPropHandleT<float> edge_length;
//add the property to mesh and name it(optional)
mesh.add_property(edge_length, "edge length");
OpenMesh::EdgeHandle eh;
float L, LL;
//write to the property
mesh.property(edge_length, eh) = L;
//read the property
LL = mesh.property(edge_length, eh);
//remove the property
mesh.remove_property(edge_length);Connectivity Query
- Getting the connectivity information
MyMesh mesh;
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh;
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh_from = mesh.from_vertex_handle(heh),
OpenMesh::VertexHandle vh_to = mesh.to_vertex_handle(heh);
OpenMesh::FaceHandle fh = mesh.face_handle(heh);
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh_next = mesh.next_halfedge_handle(heh);
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh_prev= mymesh.prev_halfedge_handle(heh);
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh_opp = mymesh.opposite_halfedge_handle(heh);Intergrated vector operations
- Using the integrated vector operations
MyMesh::Point x, y, a, b, c, d;
...
//arithmetic operations
a = x + y;
b = x - y;
c = x * 0.5;
d = y / 3.0;
...Intergrated vector operations
- Using the integrated vector operations
MyMesh::Point x, y, a, b, c, d;
...
//dot product
Scalar dot = OpenMesh::dot(x, y); //Scalar dot = x | y;
//compute the norm
Scalar norm = x.norm();
//normalize
a = x.normalize();
//cross product
MyMesh::Point cross = OpenMesh::cross(x, y); //Scalar b = x % y;
...Reference
- OpenMesh: http://www.openmesh.org