Digital Geometry Processing
Ex10-Parameterization I
Heng Liu, liu@inf.unibe.ch
Computer Graphics Group
Discrete Laplace-Beltrami
Function values sampled at mesh vertices \[\vec{f} = [f_1,f_2,\dots,f_n]\in \set{\R}^n\]
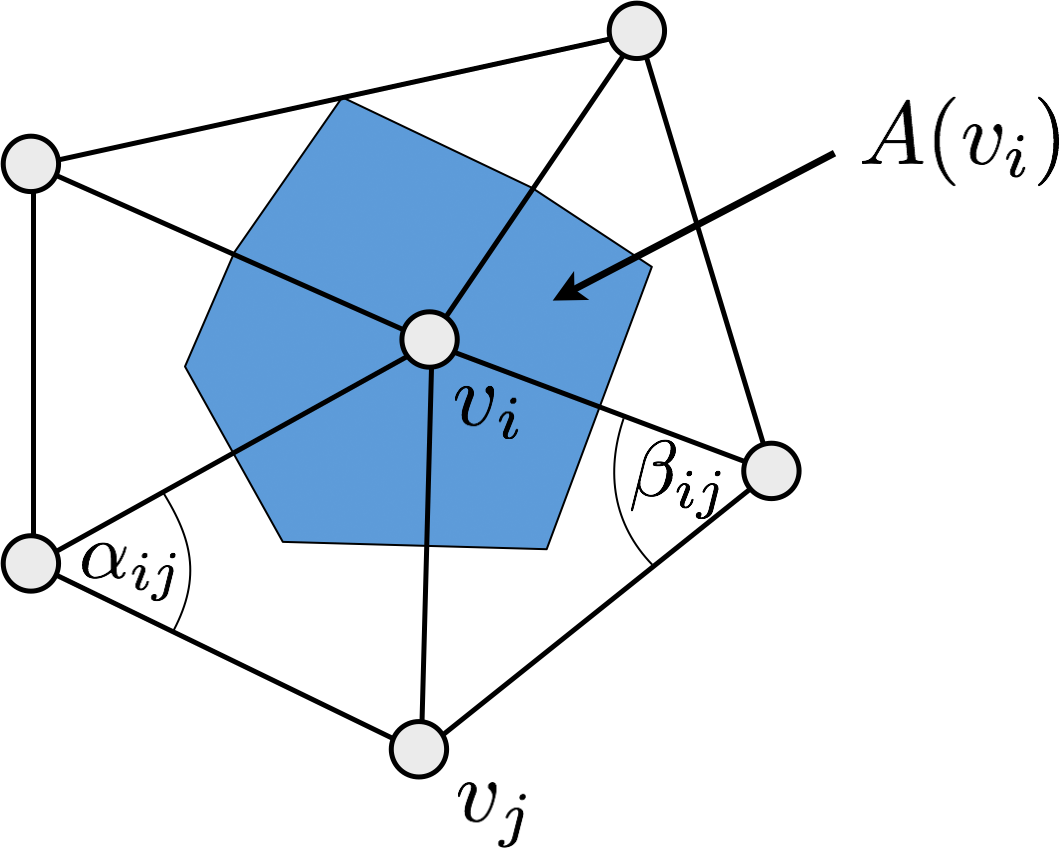
Discrete Laplace-Beltrami (per-vertex) \[\laplace_{\set{S}}f(v_i) := \frac{1}{2A_i} \sum_{v_j \in \set{N}_1\of{v_i}} (\cot\alpha_{ij} + \cot\beta_{ij}) (f\of{v_j}-f\of{v_i})\]
Discrete Laplace-Beltrami
- Discrete Laplace operator (per mesh)
- Sparse matrix \(\vec{L} = \vec{DM} \in \R^{n\times n}\)
\[\matrix{\vdots \\ \laplace_\set{S}f(v_i) \\ \vdots} = \vec{L} \cdot \matrix{\vdots \\ f(v_i) \\ \vdots}\]
Discrete Laplace-Beltrami
- Discrete Laplace operator (per mesh)
- Sparse matrix \(\vec{L} = \vec{DM} \in \R^{n\times n}\)
\[\mat{D} = \func{diag}\of{ \dots, \frac{1}{2A_i}, \dots}\]

Harmonic Functions on Surfaces
A function \(\vec{f}: \set{S} \rightarrow \R^n\) on a surface \(\set{S}\) is \(\vec{harmonic}\) if it satisfies (for each point) \[\laplace_\set{S}\vec{f} = 0\]
Discrete Laplace operator (per mesh)
- Sparse matrix \(\vec{L} = \vec{DM} \in \R^{n\times n}\)
\[\matrix{\vdots \\ \laplace_\set{S}f(v_i) \\ \vdots} = \vec{L} \cdot \matrix{\vdots \\ f(v_i) \\ \vdots} = 0\]
Harmonic Functions on Surfaces
- Fix the values of harmonic function at the vertices \(i\) and \(j\) such that \(f(x_i) = 0\) and \(f(x_j) = 1\).
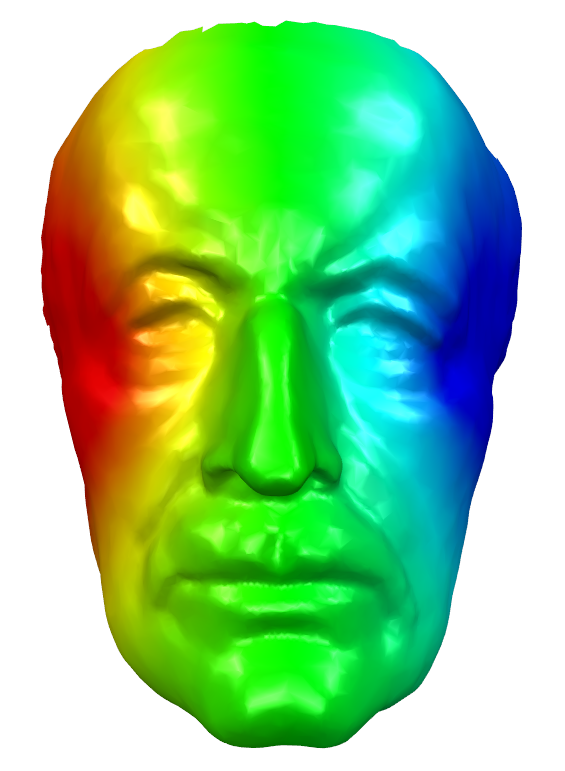

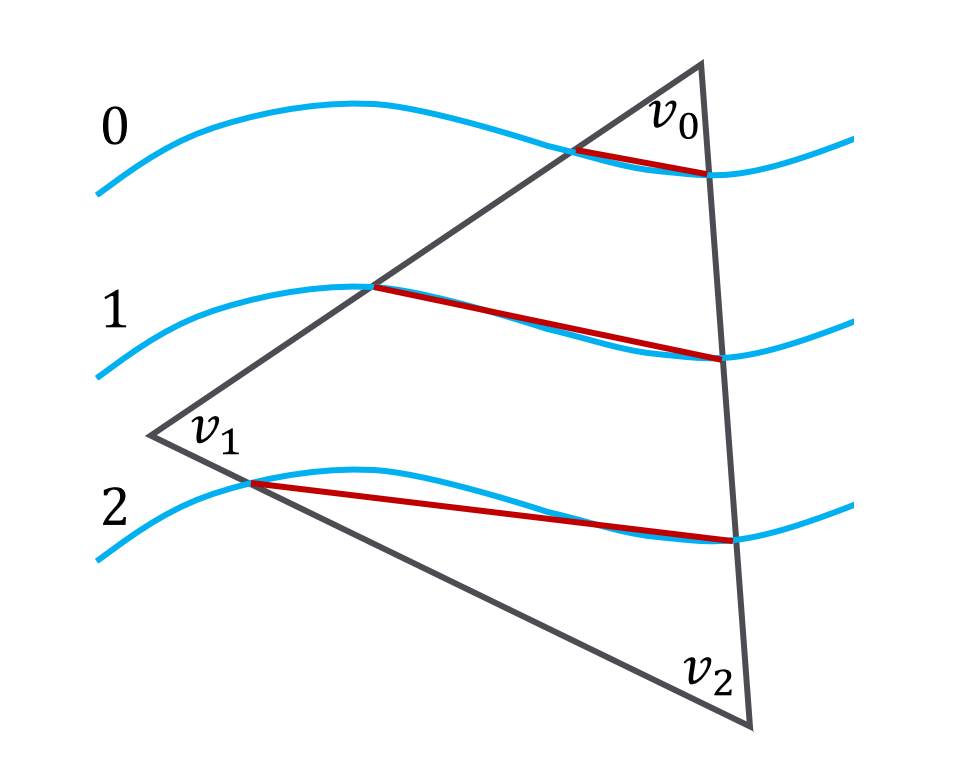
Isolines
- Isolines are lines drawn to link different places that share a common value.
Isolines
- Isolines of harmonic functions on a 3D surface
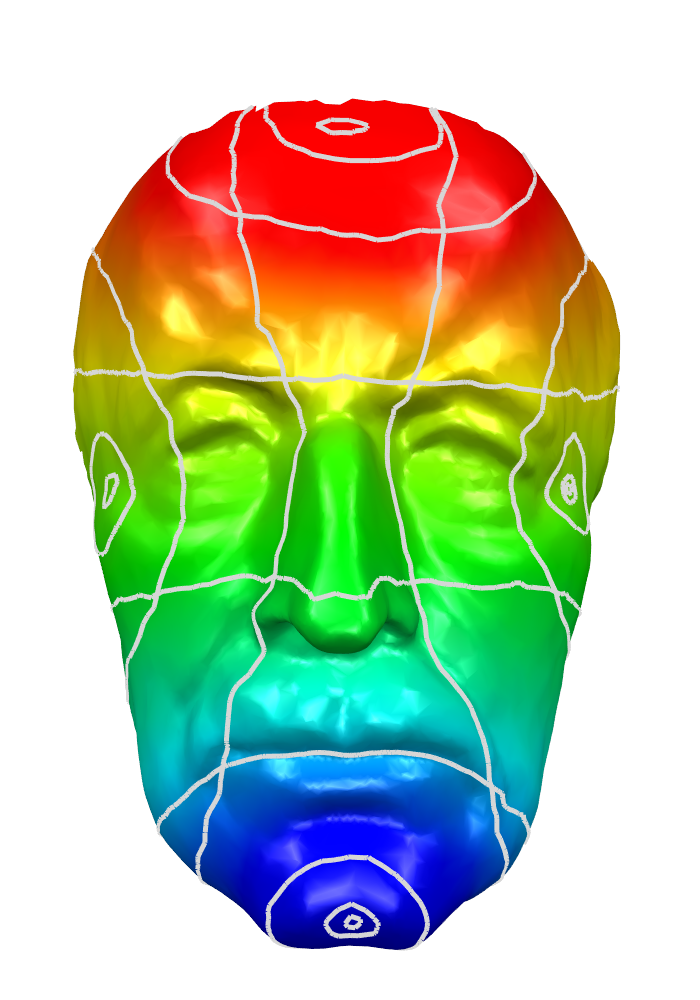
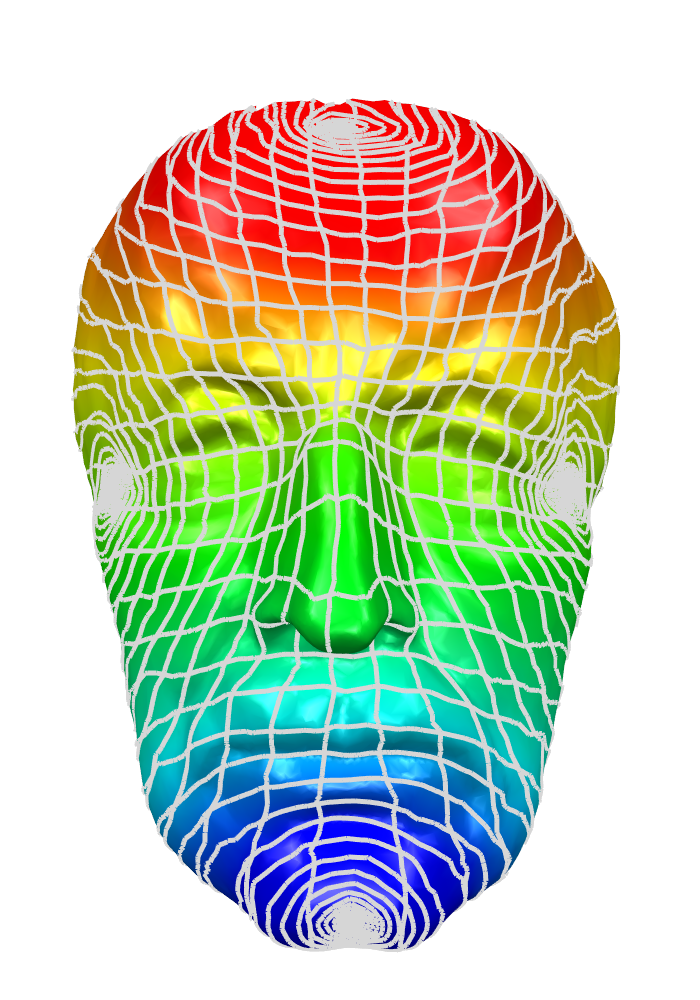



Isolines
- Isolines of harmonic functions on a 3D surface
- get_intervals_borders(): identify isolines intersecting with an edge
- add_isoline_segment(): compute intersecting point by interpolation